SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) and its successor TLS (Transport Layer Security) are security protocols that use cryptography to increase the privacy and security of data in Internet communications.
A digital certificate is a computer file that contains a set of information about the entity for which the certificate was issued. The entity can be a company, an individual, or a computer. It also contains the date of issuance, the validity period, and the public key that references the private key of the certificate.
The Digital Certificate, together with the SSL/TLS protocol, makes it possible to establish a secure channel between a web server (website, system, webmail, etc.) and a browser, ensuring that all data transmitted is protected and cannot be intercepted.
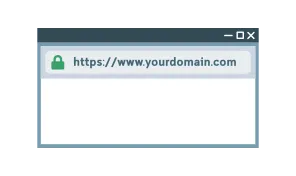
By using an SSL/TLS Certificate, you can also visually demonstrate that your Web site is trusted, authentic, and not a clone. When a valid SSL/TLS Certificate is enabled on a Web site, a padlock indicating a secure connection appears next to the URL that begins with HTTPS in the browser.
The SSL/TLS Certificate is essential for all types of Web sites and servers that need to protect data such as login information, registrations, and credit card numbers over the Internet. With digital crime on the rise, most people will not send their sensitive information through your Web site if it is not secure.
Google has launched a campaign to encourage all websites to use an SSL/TLS certificate. The Chrome browser will display the words "not secure" in the browser address bar for all websites that do not have a valid and active SSL/TLS certificate. However, if your site has SSL/TLS, it ranks higher in Google searches than sites without.